how many sample size is enough for quantitative research|30 respondents for quantitative research : consultant An increase in the power of the study requires a larger sample size (Example #2). However, increasing the effect size (Example #3) or increasing the underlying risk (Example #4) reduces . 1 Decímetros cúbicos = 100 Centilitros: 10 Decímetros cúbico.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Fidei Elegant & Modern Jewelry - DIRECT FROM LOURDE.
sample size calculator quantitative research
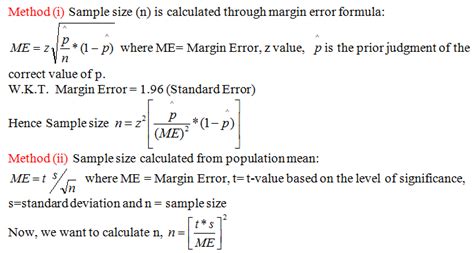
The importance of an accurate sample size calculation when designing quantitative research is well documented [1 – 3]. Without a carefully considered calculation, results can be missed, biased or just plain incorrect. How Many Participants for Quantitative Usability Studies: A Summary of Sample-Size Recommendations. Summary: 40 participants is an appropriate number for most quantitative studies, but there are cases where .The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math skills. Cochran’s formula is perhaps the most well known equation for calculating . You need to determine how big of a sample size you need so that you can be sure the quantitative data you get from a survey is reflective of your target population as a whole - and so that the decisions you make based .
An increase in the power of the study requires a larger sample size (Example #2). However, increasing the effect size (Example #3) or increasing the underlying risk (Example #4) reduces .Both small sample sizes and low effect sizes reduce the power in the study. Power, which is the probability of rejecting a false null hypothesis, is calculated as 1-β (also expressed as “1 - Type .
quantitative sampling
This paper only examines sample size considerations in quantitative research. Factors that influence sample sizes Sufficient sample size is the minimum number of . In this article, we'll answer these questions about sample size in quantitative research: Why does sample size matter? How do I determine sample size? Which sampling .Sample size is the number of observations or data points collected in a study. It is a crucial element in any statistical analysis because it is the foundation for drawing inferences and conclusions about a larger population.The importance of an accurate sample size calculation when designing quantitative research is well documented [1 . Sample size: how many participants do I need in my research? . Sullivan GM, Feinn R. Using effect size—or why the P value is not enough. J Grad Med Educ. 2012;4(3):279–282. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-12-00156.1. .
Sample size is a term used in market research to define the number of subjects included in a survey, study, or experiment. In surveys with large populations, sample size is incredibly important. . Depending on your . For example, the curve for the sample size of 20 indicates that the smaller design does not achieve 90% power until the difference is approximately 6.5. If increasing the sample size is genuinely cost prohibitive, perhaps .
Sample adequacy in qualitative inquiry pertains to the appropriateness of the sample composition and size.It is an important consideration in evaluations of the quality and trustworthiness of much qualitative research [] and is implicated – particularly for research that is situated within a post-positivist tradition and retains a degree of commitment to realist . Common Misconceptions. Some UX professionals assume that the recommendation to test with 5 users applies to interview-based studies as well. In fact, for many exploratory-research studies, 5 participants are too few.Others have been taught to recruit 5 people per persona, a rule of thumb to ensure that the sample is representative and large .Sample size is one element of research design that investigators need to consider as they plan their study. Reasons to accurately calculate the required sample size include achieving Although sample size is a consideration in qualitative research, the principles that guide the determination of sufficient sample size are different to those that are considered in quantitative research. This paper only examines sample size considerations in .
In 2006, Guest and colleagues (2006) published an article on estimating the minimum number of interviews that researchers need for studies based on qualitative data. The main finding of that article was striking: Theme 1 saturation—defined as identifying around 90% of themes in a set of qualitative interviews—could be reached within 6–12 interviews, an .
These research objectives are typical of much qualitative heath research. The sample size of the datasets used varied from 14 to 132 interviews and 1 to 40 focus groups. . Since a statistical formula may be seen as akin to a power calculation familiar to quantitative researchers, we feel that this may provide a misleading veil of scientific .
Researchers often find it difficult to justify their sample size (i.e., a number of participants, observations, or any combination thereof). In this review article six possible approaches are discussed that can be used to justify the sample size in a quantitative study (see Table 1).This is not an exhaustive overview, but it includes the most common and . Approaches to sample size calculation according to study design are presented with examples in health research. For sample size estimation, researchers need to (1) provide information regarding the statistical analysis to be applied, (2) determine acceptable precision levels, (3) decide on study power, (4) specify the confidence level, and (5 . Health services researchers face two obstacles to sample size calculation: inaccessible, highly specialised or overly technical literature, and difficulty securing methodologists during the planning stages of research. The purpose of this article is to provide pragmatic sample size calculation guidance for researchers who are designing a health .
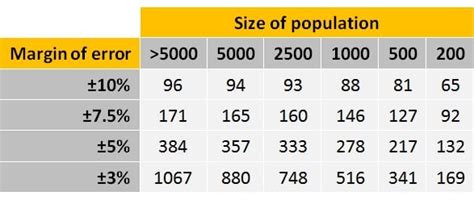
minimum sample size is 100
This free sample size calculator determines the sample size required to meet a given set of constraints. Also, learn more about population standard deviation.The table shown on the right can be used in a two-sample t-test to estimate the sample sizes of an experimental group and a control group that are of equal size, that is, the total number of individuals in the trial is twice that of the number given, and the desired significance level is 0.05. [4] The parameters used are: The desired statistical power of the trial, shown in column to the .
Sample Size Calculation. Statisticians have devised quantitative ways to find a good sample size. You want a large enough sample to have a reasonable chance of detecting a meaningful effect when it exists but not too large to be .The Sampling Issues in Quantitative Research Ali DELİCE* Abstract A concern for generalization dominates quantitative research. For generalizability and re-peatability, identification of sample size is essential. The present study investigates 90 qu-alitative master’s theses submitted for the Primary and Secondary School Science and Considering the difficulties and highly conflicting perspectives regarding sample size calculation, and even whether it should be calculated at all, this study follows the practical advice presented in studies like Bacchetti's (2010) and seeks to include a large enough sample so as to help account for outliers which can easily skew descriptive . One of the major issues in planning a research is the decision as to how a sample and the method to be employed to select the estimated sample in order to meet the objective of the research.
4) Use best practice guidelines to calculate sample size. There are many established guidelines and formulas that can help you in determining the right sample size. The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math skills. Cochran’s . The literature recommends a large sample size that can easily yield a new and rich understanding of the phenomenon, and at the same time small enough to obtain deep and case-oriented data [27].
A common question in qualitative research involves the sample size. The question of saturation is always at the forefront. . there is variation in sample size and the number of participants necessary to reach data saturation. . A., & Johnson, L. (2006). How many interviews are enough?: An experiment with data saturation and variability .
Research methodology, Sample size, Generalization, Interview research, Qualitative research, . The related concepts of generalization and sample size (N size) are from quantitative work (see for example, Teo, 2013). . a sample size ample enough to allow accurate estimation of how likely (probable) it is thatA large sample size typically provides enough statistical power to find important differences in a population. In many fields, experts consider a large sample size to include several hundred participants. Getting a "large" sample size can depend on factors like your field of study, research goal, or type of study.
Abstract. Thematic analysis is frequently used to analyse qualitative data in psychology, healthcare, social research and beyond. An important stage in planning a study is determining how large a sample size may be required, however current guidelines for thematic analysis are varied, ranging from around 2 to over 400 and it is unclear how to choose a value . Gale Academic OneFile includes Sample size in quantitative research: Sample size will by Susan B. Fowler and Valerie Lapp. Click to explore. Use this link to get back to this page. 1. Convenience sampling. A convenience sample simply includes the individuals who happen to be most accessible to the researcher. This is an easy and inexpensive way to gather initial data, but there is no way to tell if the sample is representative of the population, so it can’t produce generalizable results. Convenience samples are at risk for both sampling bias .
minimum sample size for statistical analysis
SAMPLING. Sampling can be defined as the process through which individuals or sampling units are selected from the sample frame. The sampling strategy needs to be specified in advance, given that the sampling method may affect the sample size estimation. 1,5 Without a rigorous sampling plan the estimates derived from the study may be biased (selection bias). 3
how to calculate sample size in research
Conoce los resultados de los sorteos de lotería de ANIMALIT.
how many sample size is enough for quantitative research|30 respondents for quantitative research